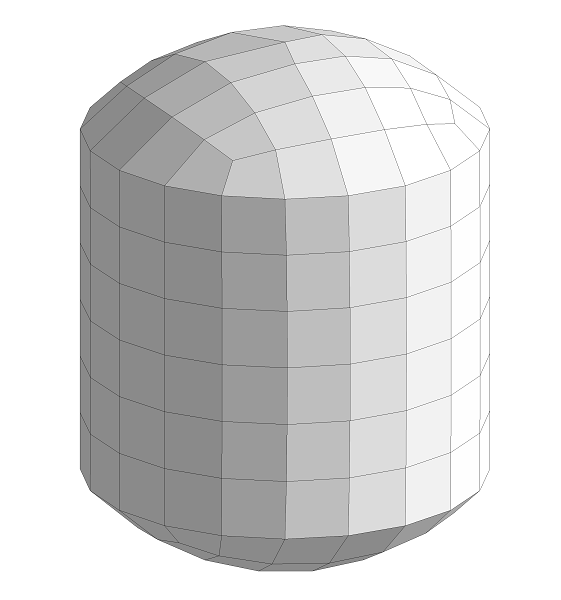
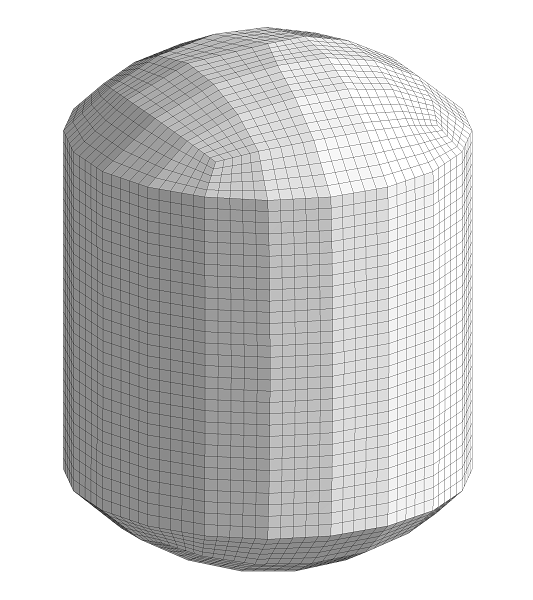
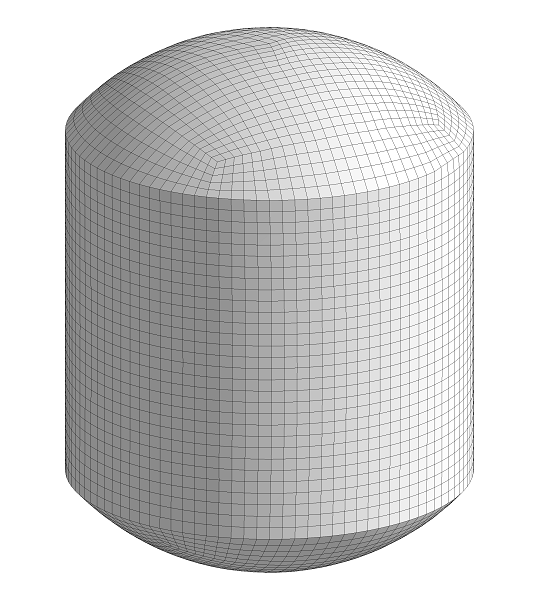
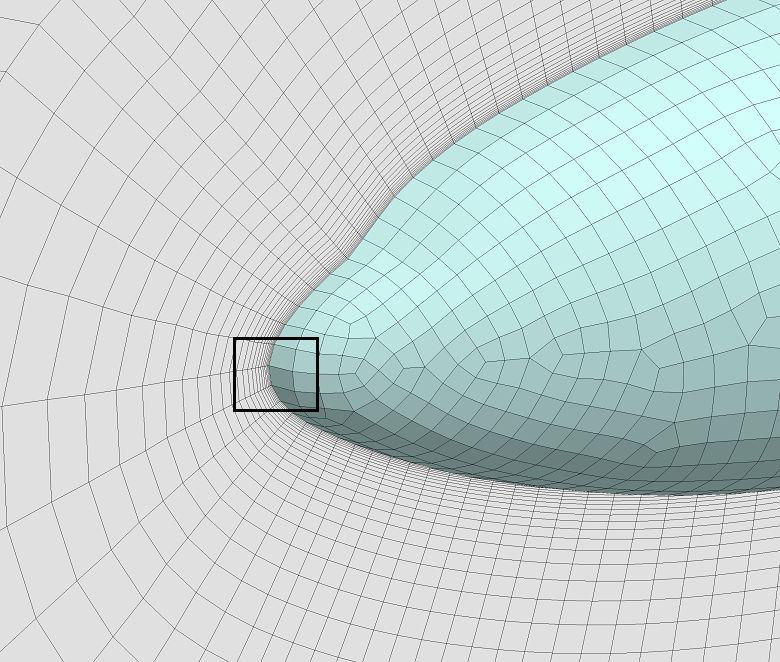
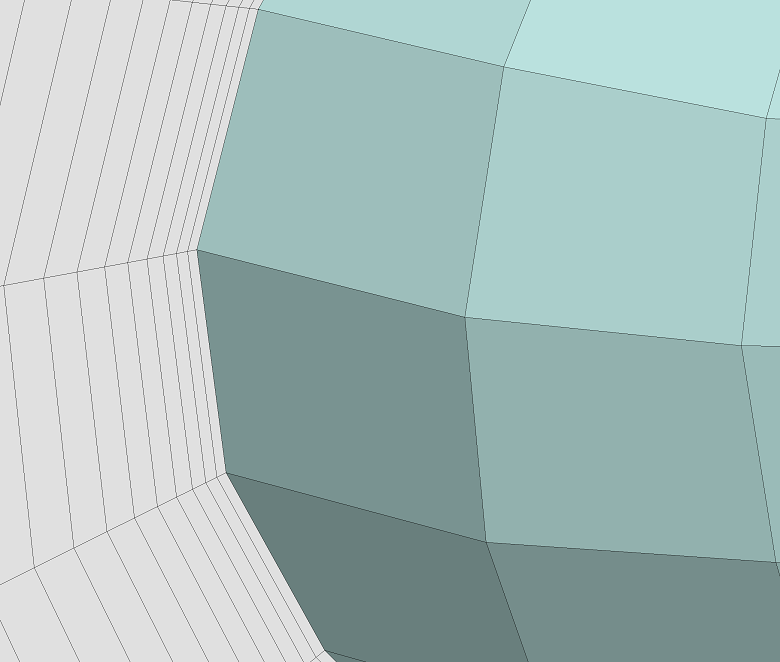
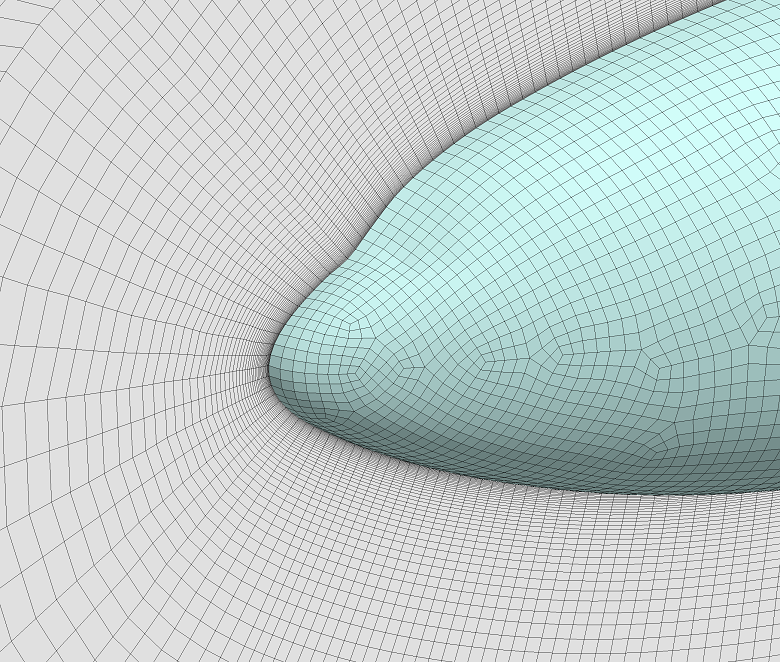
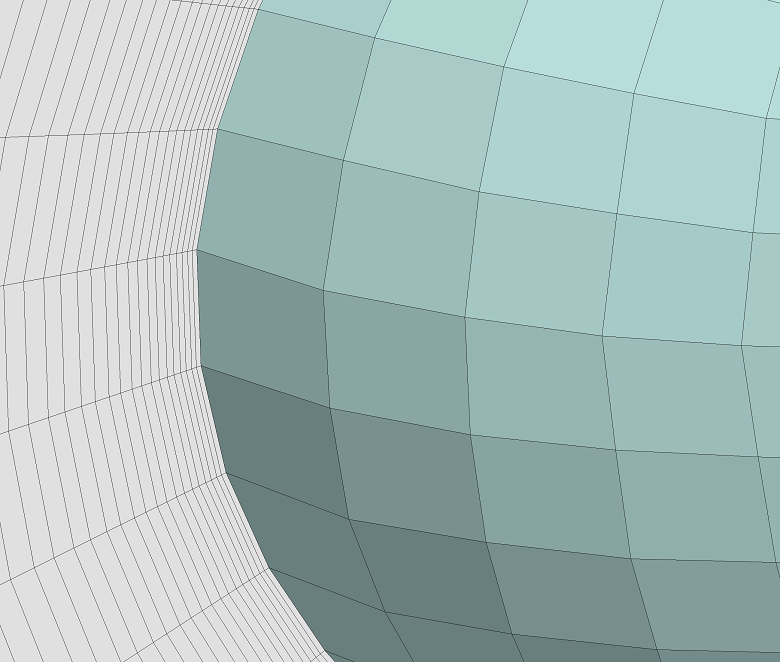
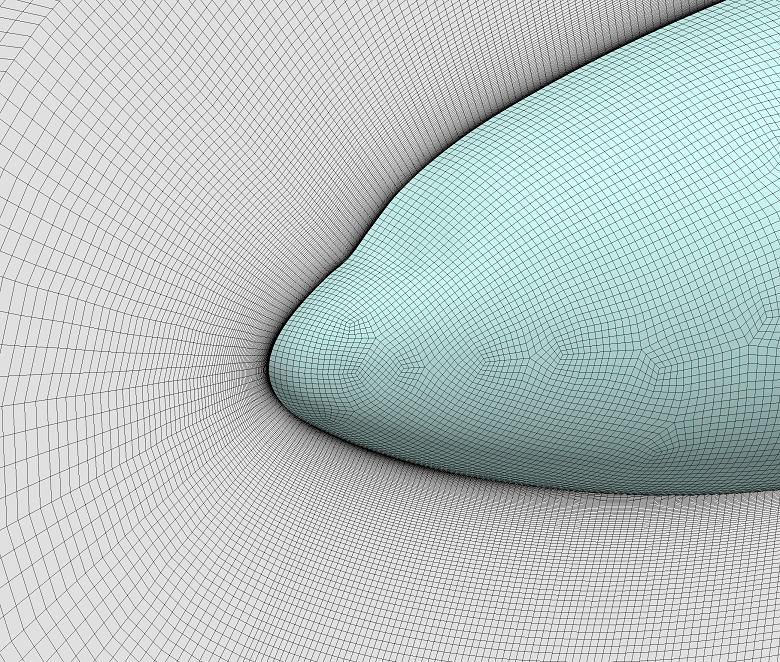
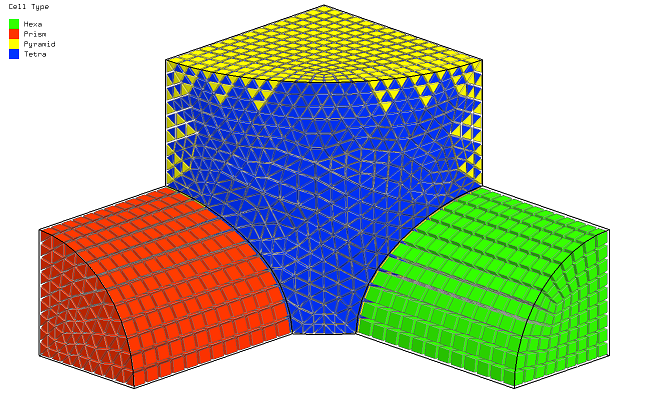
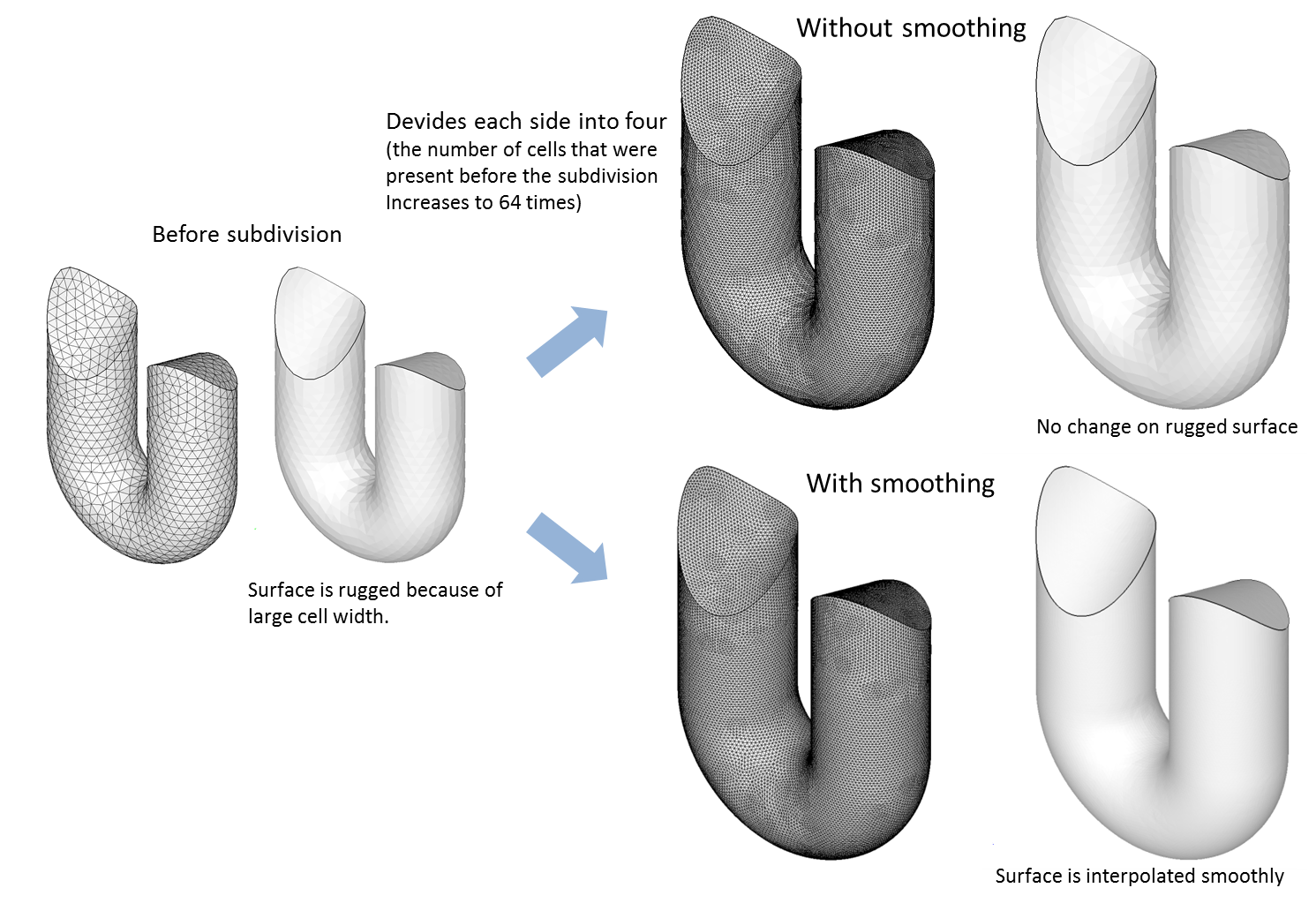
▊Example of an unstructured hexahedron grid (1)
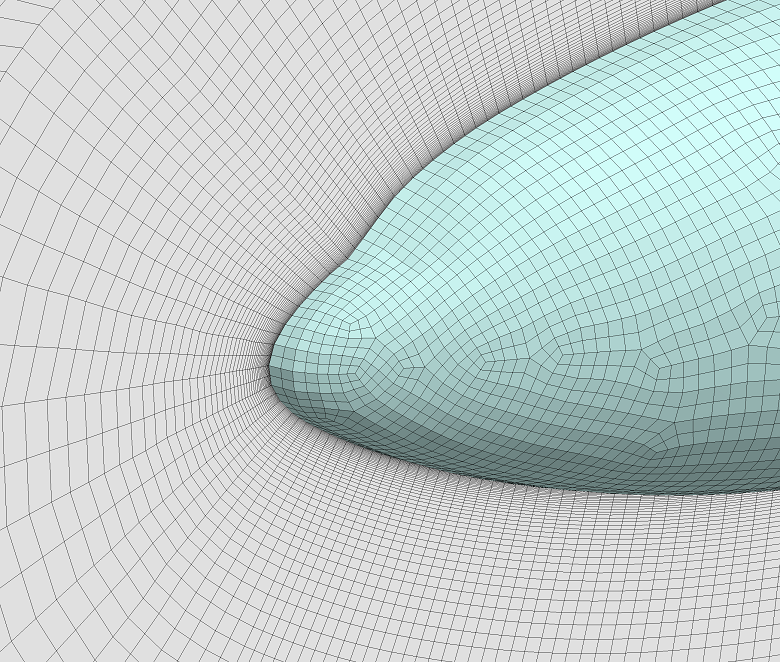
Subdivide by an arbitrary number of divisions for structured grids, unstructured grids, and hybrid grids.
Find a position in which to insert a new node using interpolation from the original grid and the subdivided smooth boundary shape.
Leave the node position in the original grid unchanged.
Specify the feature angle to be maintained.
Fit the surface shape by reading STL data if needed.
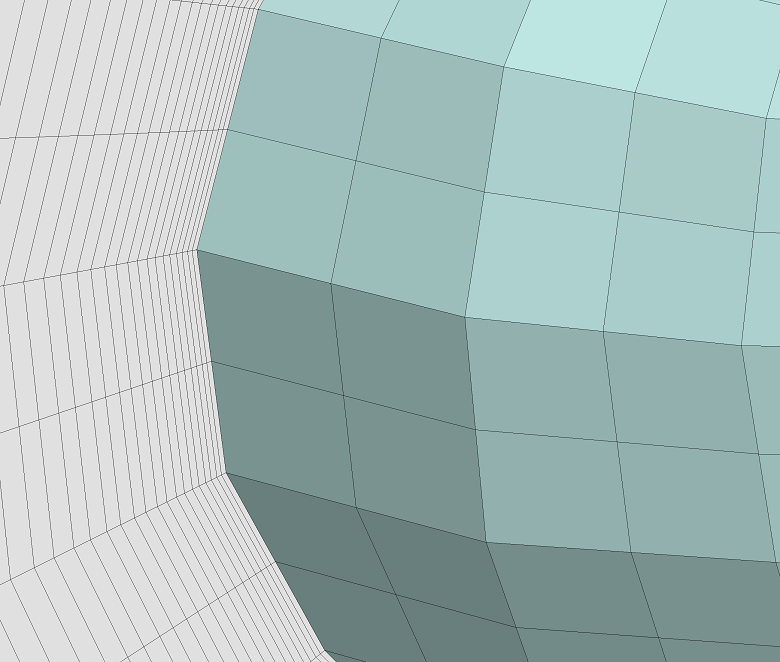
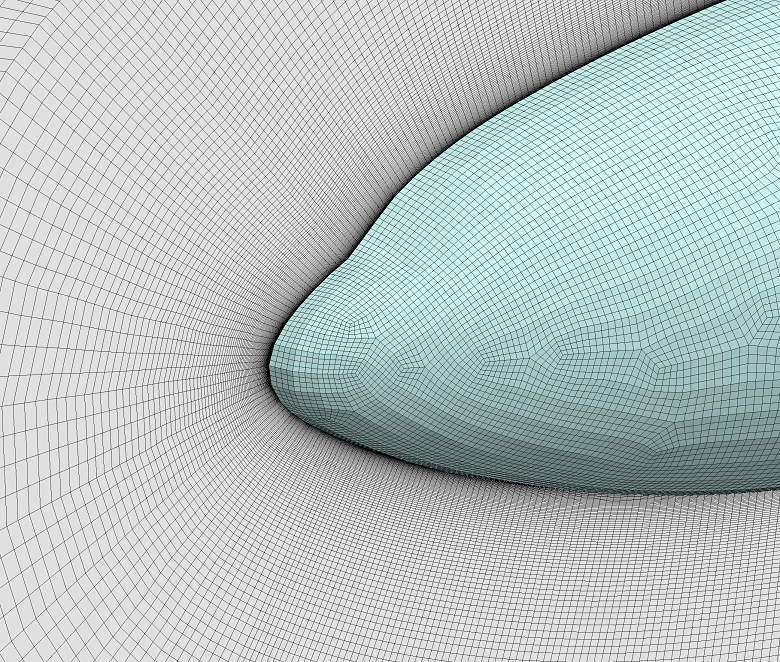
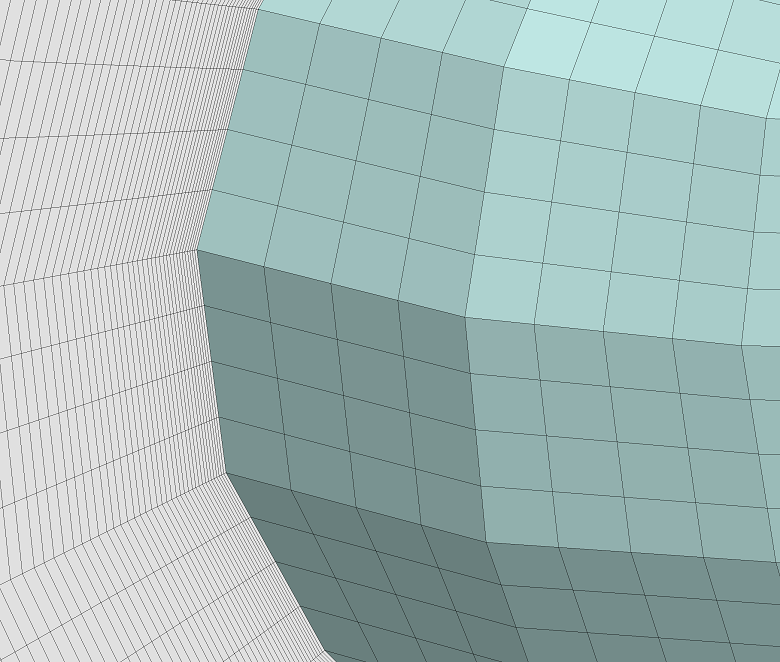
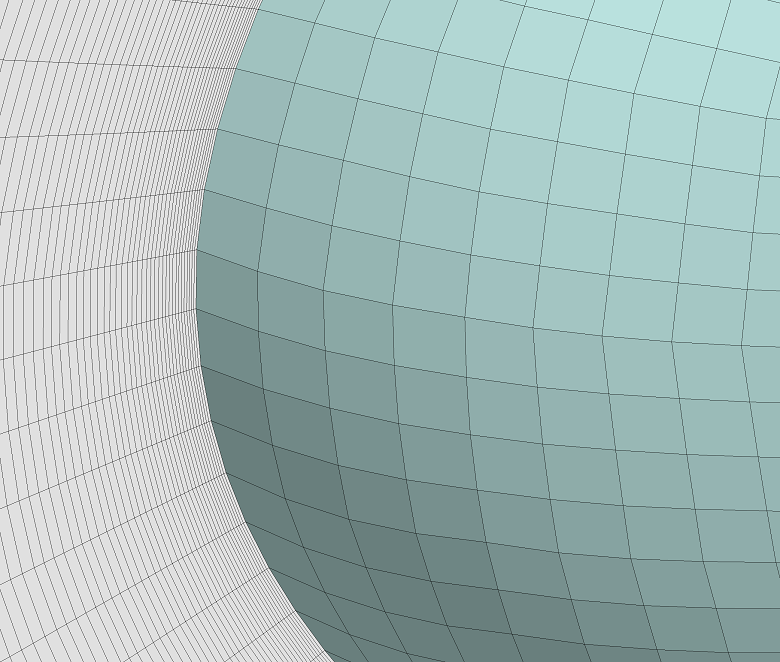
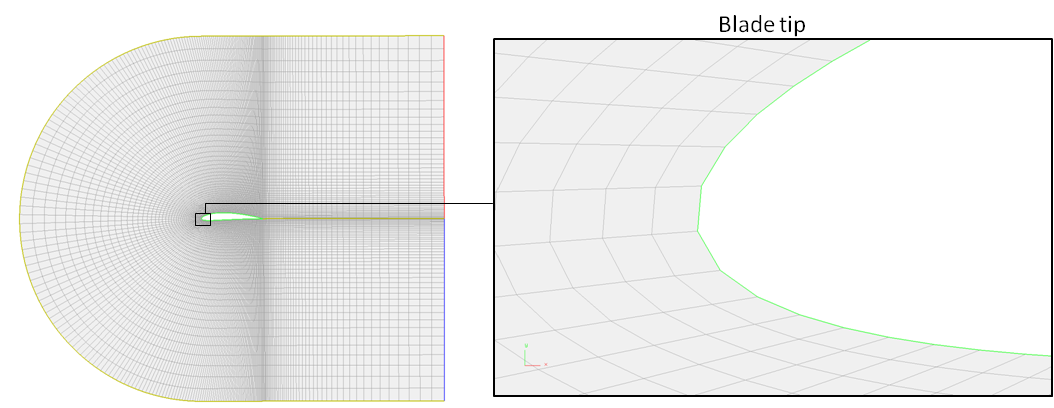
▊ Example of an unstructured hexahedron grid (2)
▶ Two-division
▶ Four-division
Increase the grating density without returning to CAD data.
Easily prepare a complete set of data of differing resolution grids when investigating the convergence properties of a grid.
Greatly shorten the amount of time required to prepare mesh generation in large-scale calculations.
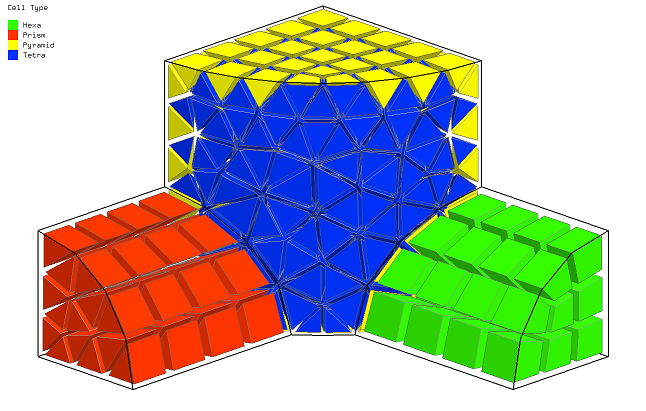
▊Example of tetrahedron unstructured grid
 QuickMesh
QuickMesh